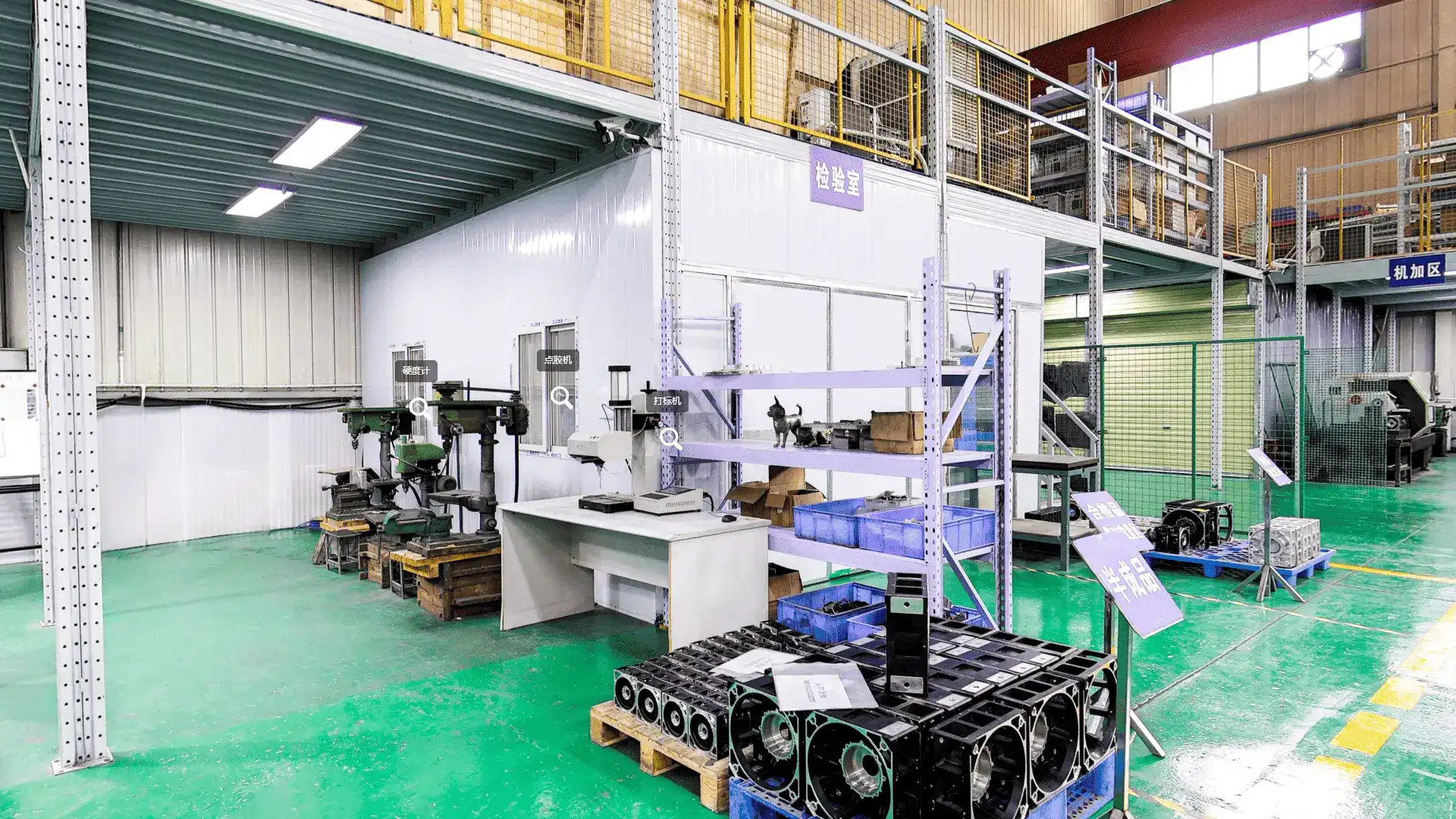
Sand Casting
Sand Casting
 VIEW MORECasting Filter Element
VIEW MORECasting Filter Element VIEW MORECast Turbine
VIEW MORECast Turbine VIEW MORESand Casting Dome Lampshade
VIEW MORESand Casting Dome Lampshade VIEW MORECast Coupling Disc A356-T6
VIEW MORECast Coupling Disc A356-T6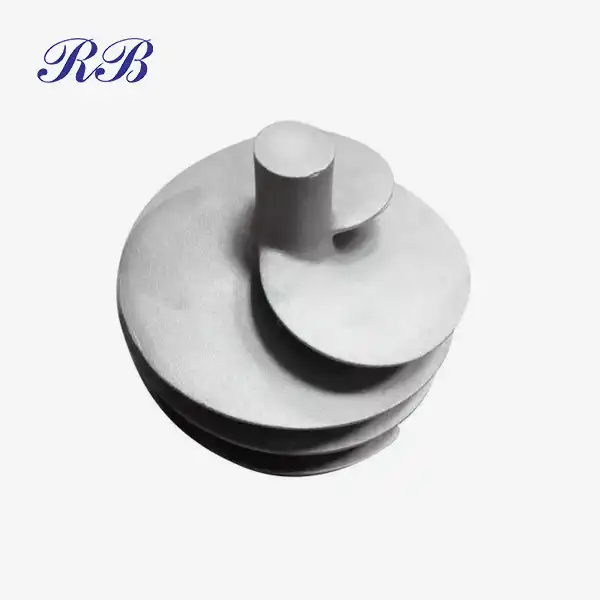 VIEW MOREKinetic Sand Aluminum Casting
VIEW MOREKinetic Sand Aluminum Casting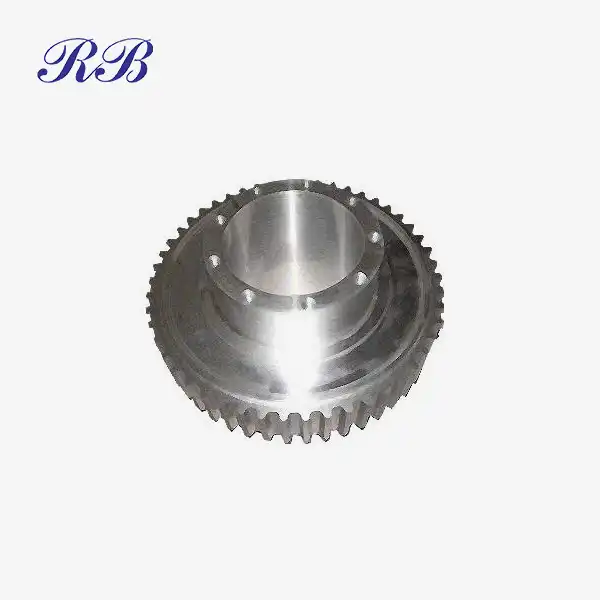 VIEW MOREKinetic Sand Casting
VIEW MOREKinetic Sand Casting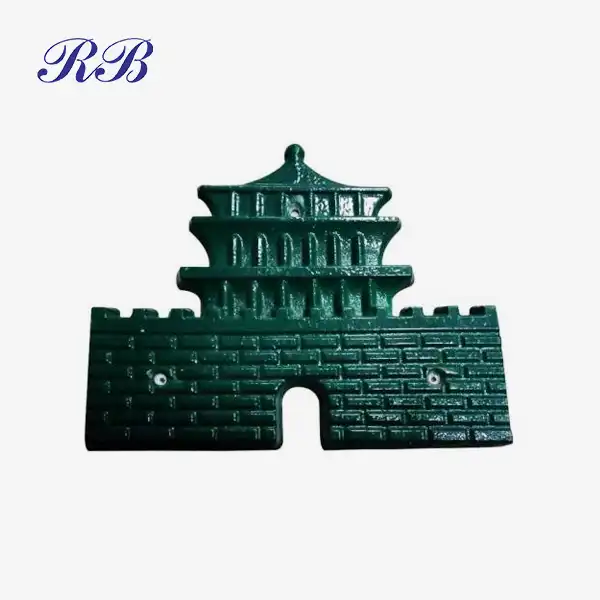 VIEW MOREDecorative Metal Casting
VIEW MOREDecorative Metal Casting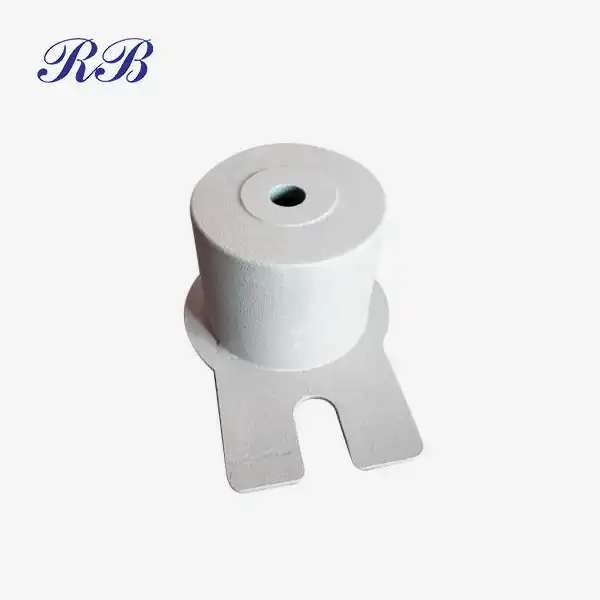 VIEW MORELow Pressure Sand Casting Parts
VIEW MORELow Pressure Sand Casting Parts
Key Features of the Sand Casting Process:
① Mold Creation: The process begins with the preparation of a mold made from a mixture of sand, clay, and water. The sand is compacted around a pattern (the object to be cast) to form a mold cavity. The pattern is then removed, leaving a hollow impression in the sand.
② Melting the Metal: The metal to be cast, typically aluminum, iron, or steel, is melted in a furnace until it reaches a liquid state. The temperature and composition of the molten metal are carefully controlled to ensure optimal casting properties.
③ Pouring the Metal: Once the metal is molten, it is poured into the mold cavity. Gravity allows the molten metal to flow into the intricate details of the mold, filling it completely.
④ Cooling and Solidification: After the mold is filled, the molten metal is allowed to cool and solidify. The cooling time can vary depending on the thickness of the casting and the type of metal used.
⑤ Mold Removal: Once the metal has solidified, the sand mold is broken away to reveal the finished casting. The casting may require additional finishing processes, such as machining or surface treatment, to achieve the desired specifications.

Advantages of Sand Casting:
(1) Cost-Effective: Sand casting is one of the most economical casting methods, particularly for low to medium production runs. The materials used for molds are inexpensive, and the process can be easily scaled.
(2) Versatility: This method can accommodate a wide range of metals and alloys, making it suitable for various applications.
(3) Complex Shapes: Sand casting allows for the production of intricate shapes and designs that may be difficult to achieve with other casting methods.
(4) Large Parts: The sand casting process is capable of producing large components, which is advantageous in industries that require heavy machinery parts or large structural elements.
Sand casting remains a fundamental process in metalworking, providing manufacturers with a reliable and efficient method for producing high-quality metal components. Its adaptability and cost-effectiveness make it a preferred choice for many applications in today’s manufacturing landscape.