Stainless Steel
Stainless Steel
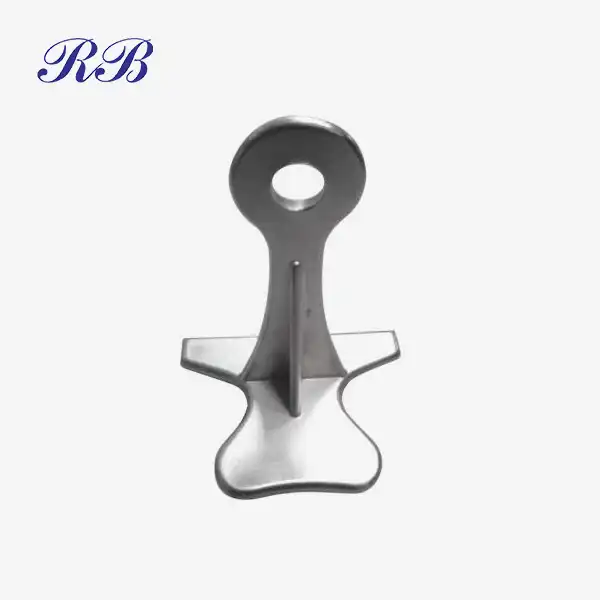 VIEW MORECustom Casting Brackets
VIEW MORECustom Casting Brackets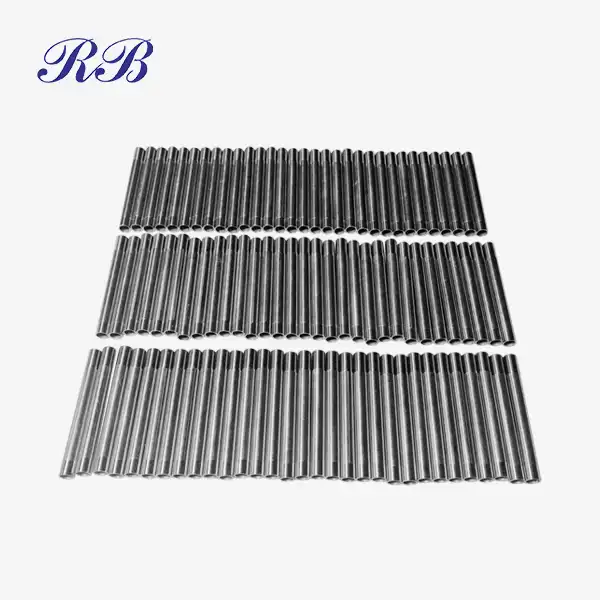 VIEW MOREStainless Steel Processing Drainage Pipe
VIEW MOREStainless Steel Processing Drainage Pipe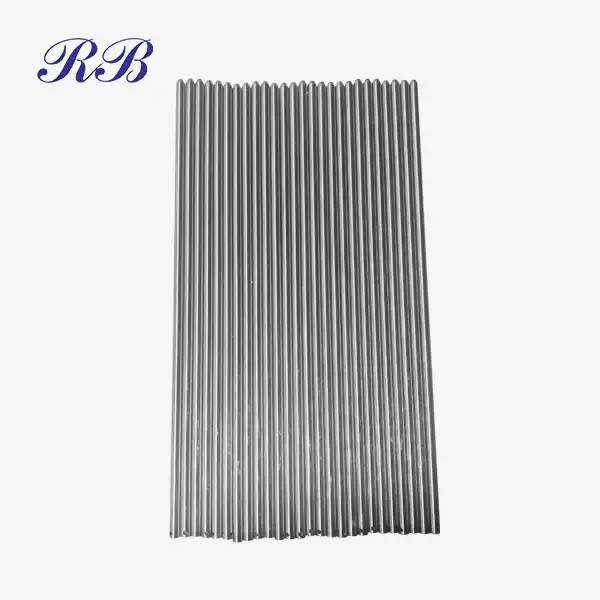 VIEW MOREStainless Steel Drive Shaft
VIEW MOREStainless Steel Drive Shaft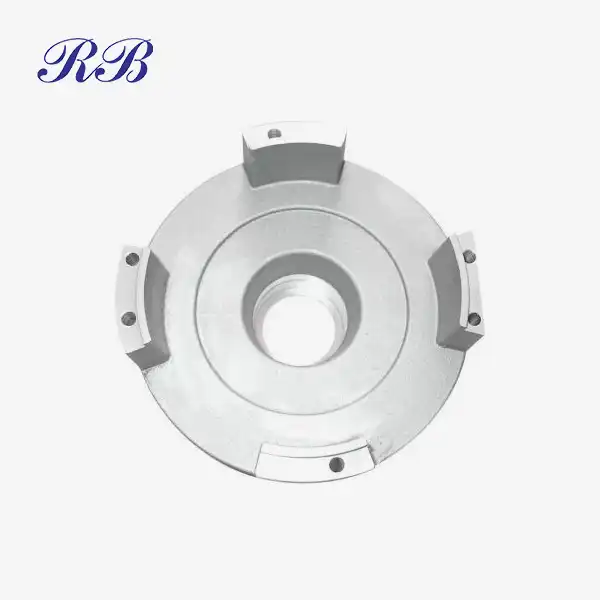 VIEW MOREStainless Steel Flanges
VIEW MOREStainless Steel Flanges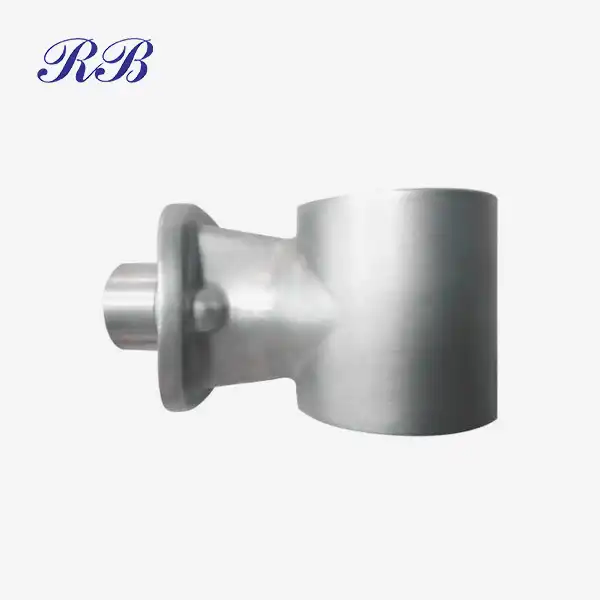 VIEW MORECast Motor Base
VIEW MORECast Motor Base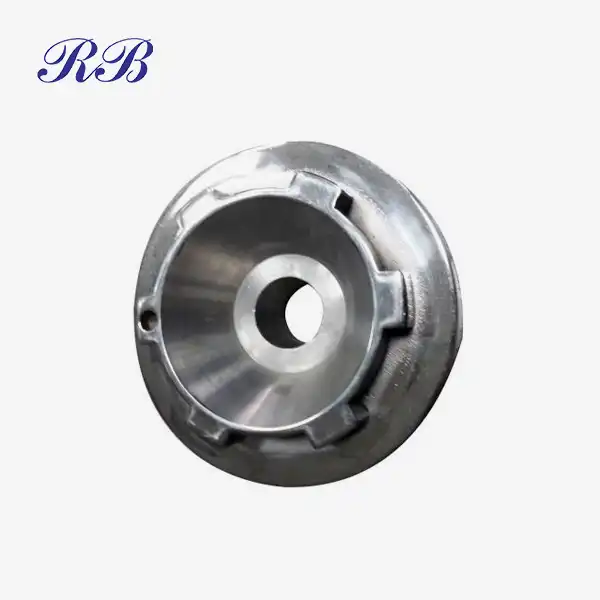 VIEW MOREThreaded Floor Flange
VIEW MOREThreaded Floor Flange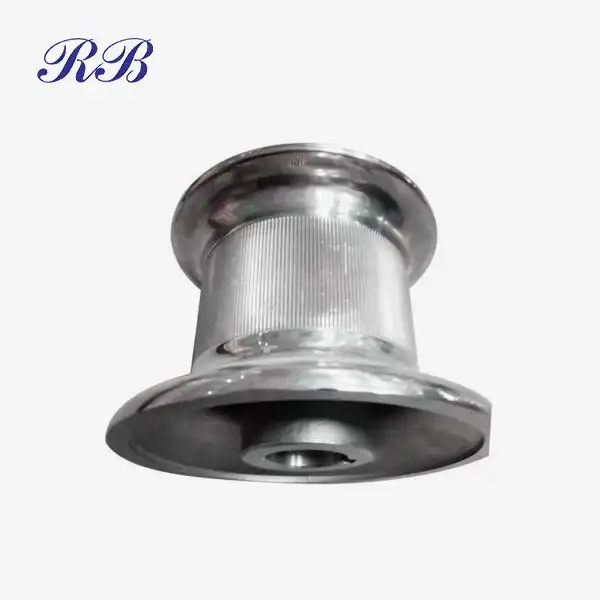 VIEW MOREMarine Stainless Steel Castings
VIEW MOREMarine Stainless Steel Castings
Key Stages of the Stainless Steel Production Process:
① Raw Material Preparation: The process begins with the selection of high-quality raw materials. The primary components include iron ore, chromium, nickel, and other alloying elements. These materials are sourced from reputable suppliers to ensure the integrity of the final product.
② Melting: The raw materials are then melted in an electric arc furnace (EAF) or a basic oxygen furnace (BOF). In the EAF, scrap stainless steel and alloying elements are added to the furnace, where they are melted at high temperatures. The BOF process involves converting molten iron into stainless steel by blowing oxygen into the molten metal to reduce carbon content.
③ Alloying: After melting, alloying elements are added to achieve the desired composition. The specific amounts of chromium, nickel, and other elements are carefully controlled to produce different grades of stainless steel, each with unique properties suited for various applications.
④ Casting: The molten stainless steel is then cast into semi-finished forms, such as slabs, billets, or blooms, through continuous casting or ingot casting methods. Continuous casting is preferred for its efficiency and ability to produce uniform shapes.
⑤ Hot Working: The cast stainless steel is subjected to hot working processes, such as rolling or forging, to shape it into the desired dimensions. Hot working enhances the material's mechanical properties and refines its microstructure.
⑥ Heat Treatment: Depending on the grade and intended application, heat treatment processes such as annealing may be applied to relieve stresses and improve corrosion resistance. This step is crucial for achieving the desired hardness and ductility.
⑦ Cold Working: For certain applications, further cold working processes, such as cold rolling or drawing, may be employed to enhance surface finish and dimensional accuracy.
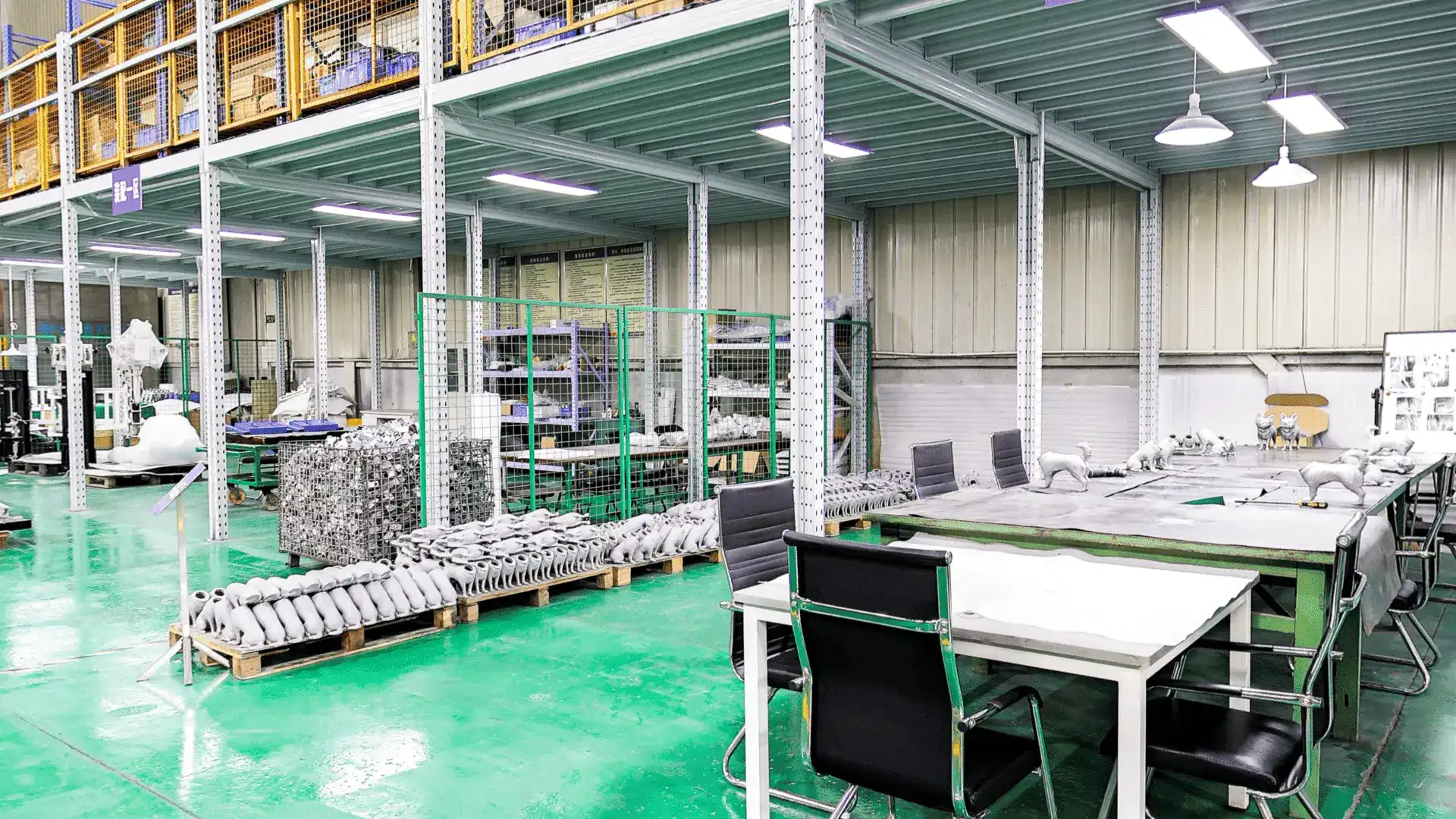
⑧ Finishing: The final stage involves surface finishing treatments, which may include polishing, passivation, or coating. These processes improve the aesthetic appearance and corrosion resistance of the stainless steel.
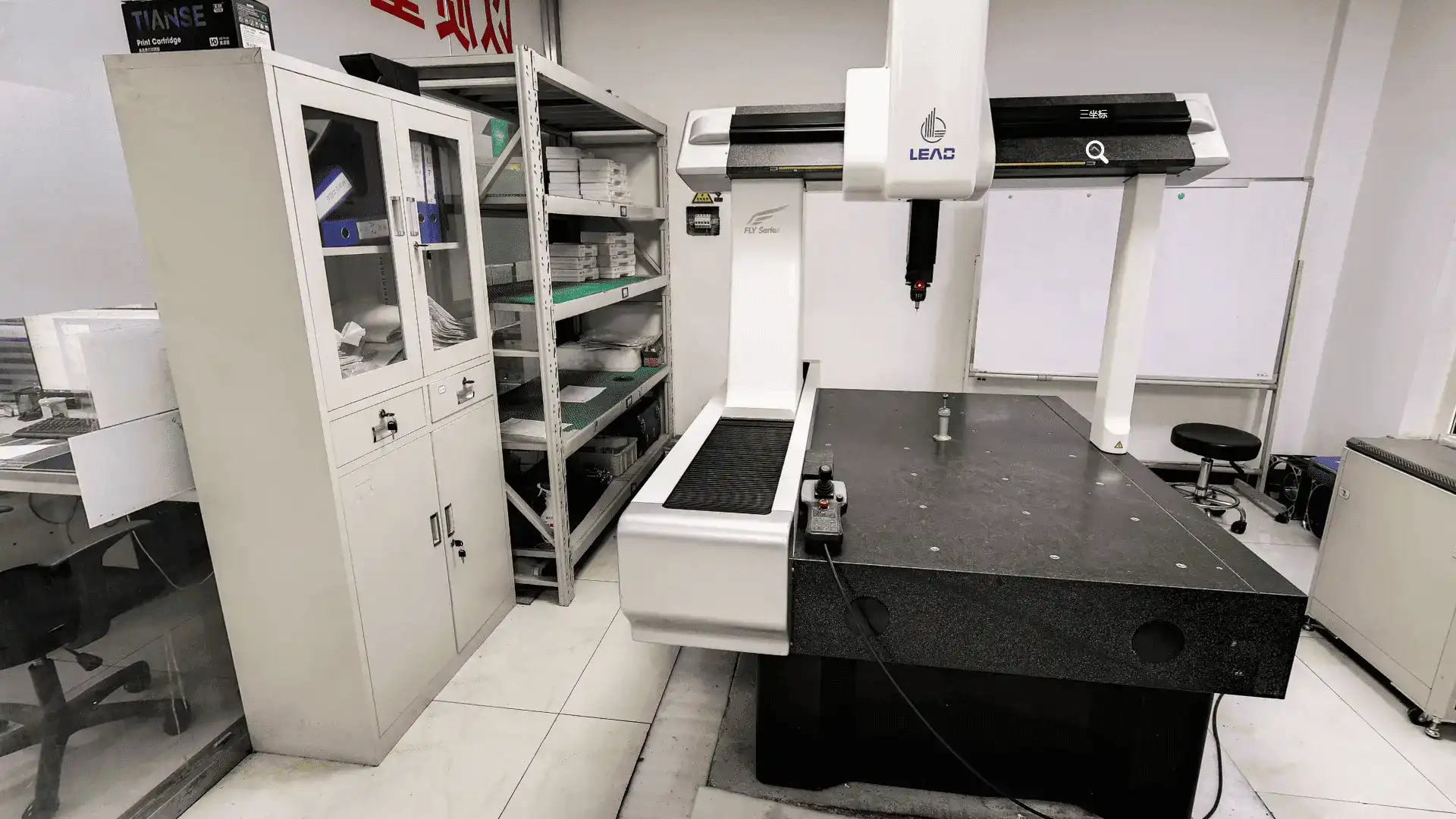
⑨ Quality Control: Throughout the production process, rigorous quality control measures are implemented to ensure that the stainless steel meets industry standards and specifications. This includes testing for mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, and surface quality.

By following these meticulous steps, manufacturers can produce high-quality stainless steel that meets the diverse needs of various industries. The versatility and durability of stainless steel make it an essential material in modern manufacturing and construction.